In today’s rapidly evolving marketplace, the push toward sustainable energy solutions has never been more critical. As environmental concerns escalate and regulatory pressures increase, businesses are increasingly recognizing the necessity of adopting renewable energy sources. Renewable energy not only helps mitigate the impact of climate change but also positions companies as responsible and forward-thinking entities.
By integrating sustainable energy practices, businesses can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, enhance their brand image, and meet the growing demand from eco-conscious consumers.
Moreover, the transition to renewable energy is becoming a pivotal factor in driving innovation and competitiveness within various industries. Companies that embrace renewable energy solutions are better equipped to navigate the complexities of energy dependency and volatility in fossil fuel markets. This proactive approach not only ensures long-term sustainability but also opens up new avenues for growth and development. As leaders in their respective fields, businesses play a crucial role in accelerating the renewable energy transition, setting standards, and inspiring others to follow suit.
The Challenge of Affordability
Despite the clear benefits, one of the most significant barriers businesses face when considering renewable energy is the perceived high cost of implementation. Many organizations operate under the misconception that transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind is prohibitively expensive. This belief often stems from outdated information and a lack of awareness about the advancements and cost reductions in renewable technologies.
However, the reality is that the balance between initial investment and long-term savings often tilts in favor of renewable energy. Over the past decade, the costs associated with renewable energy technologies have plummeted, making them more accessible and affordable for businesses of all sizes. Additionally, numerous financing options, incentives, and government grants are available to help offset the upfront costs.
By carefully evaluating the long-term financial benefits, such as reduced energy bills and increased property value, businesses can make informed decisions that not only support their sustainability goals but also enhance their financial performance.
This article aims to demystify the affordability of renewable energy solutions for businesses, providing a comprehensive overview of cost-effective options available today. We will explore a variety of renewable energy sources, including solar and wind, and delve into additional alternatives that offer practical and budget-friendly solutions for businesses seeking to make the switch.
Our focus will be on highlighting strategies and technologies that enable businesses to implement renewable energy without compromising their financial stability. From understanding the financial incentives and financing models to examining real-world case studies of successful implementations, this article will serve as a valuable guide for businesses looking to adopt renewable energy on a budget.
By emphasizing affordability and practicality, we aim to empower businesses to take actionable steps toward a more sustainable and economically viable energy future.
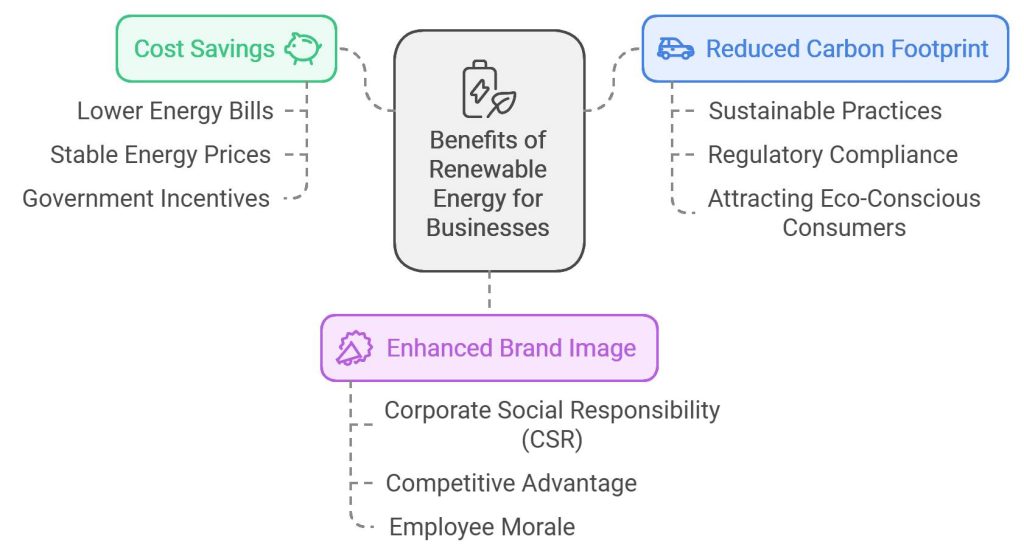
Benefits of Adopting Renewable Energy
Adopting renewable energy solutions offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, ranging from significant cost savings to enhanced corporate reputation. Below, we delve into the key advantages that make renewable energy an attractive option for businesses aiming to thrive sustainably.
Cost Savings and Financial Incentives
One of the most compelling reasons businesses transition to renewable energy is the potential for substantial cost savings. By reducing reliance on traditional energy sources, companies can lower their monthly energy bills and improve their bottom line.
Reduction in Energy Bills
Renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, generate electricity that can significantly decrease or even eliminate a business’s dependence on grid power. Over time, the initial investment in renewable technology pays off through reduced energy expenses.
Projected Energy Bill Savings with Solar Installation
| System Size (kW) | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Energy Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 75,000 | 10,000 | 7.5 |
| 100 | 140,000 | 20,000 | 7 |
| 200 | 270,000 | 40,000 | 6.75 |
Table 1 illustrates the potential savings and payback periods for businesses investing in solar energy systems of varying sizes.
“Renewable energy is not only good for the planet, but it also makes good business sense. Investing in sustainable energy solutions can lead to significant cost savings and enhance a company’s reputation.”
— Jane Doe, Sustainability Expert
Availability of Grants, Tax Credits, and Rebates
Governments and organizations worldwide offer numerous financial incentives to encourage businesses to adopt renewable energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with renewable energy installations.
Common Financial Incentives for Renewable Energy Adoption
| Incentive Type | Description | Potential Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Tax Credits | Percentage of installation costs refundable on taxes | Up to 26% |
| State Grants | Direct financial support for renewable projects | Varies by state |
| Rebates from Utilities | Cash back or discounts on energy system purchases | Up to 30% |
| Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) | Tradable certificates representing renewable energy generation | Market-dependent |
Table 2 outlines various financial incentives available to businesses, highlighting potential savings that can make renewable energy projects more affordable.
Environmental Impact and Corporate Responsibility
Beyond financial benefits, adopting renewable energy aligns with broader environmental and corporate responsibility goals, enhancing a company’s reputation and commitment to sustainability.
Lowering Carbon Footprint
Transitioning to renewable energy significantly reduces a business’s carbon emissions. This not only contributes to the fight against climate change but also meets the increasing demand for sustainable practices from stakeholders.
Figure 1: Carbon Emissions Reduction with Renewable Energy Adoption
Figure 1 showcases the potential reduction in carbon emissions when a business adopts renewable energy sources compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Enhancing Corporate Sustainability Profiles
Embracing renewable energy strengthens a company’s sustainability profile, making it more attractive to investors, customers, and partners who prioritize environmental responsibility.
Energy Independence and Reliability
Renewable energy provides businesses with greater control over their energy sources, enhancing reliability and reducing vulnerability to external factors.
Protection Against Energy Price Volatility
Traditional energy prices are subject to market fluctuations and geopolitical tensions, which can lead to unpredictable costs. Renewable energy systems offer a stable and predictable energy cost structure.
Energy Price Stability: Renewable vs. Traditional Sources
| Energy Source | Price Stability (USD per MWh) | Price Volatility (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar | 50 | 5 |
| Wind | 55 | 6 |
| Natural Gas | 70 | 20 |
| Oil | 90 | 25 |
Table 3 compares the price stability and volatility of renewable energy sources versus traditional fossil fuels, highlighting the financial predictability of renewables.
Increased Energy Security
By generating their own energy, businesses reduce dependence on external suppliers, ensuring a more reliable energy supply even during disruptions.
Brand Image and Competitive Advantage
Adopting renewable energy can significantly enhance a company’s brand image, positioning it as a leader in sustainability and attracting a loyal customer base.
Attracting Eco-Conscious Customers and Partners
Today’s consumers and business partners are increasingly eco-conscious, preferring to engage with companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Renewable energy adoption serves as a tangible proof of this commitment.
Differentiating from Competitors
In competitive markets, having a renewable energy strategy can set a business apart from its competitors, offering a unique selling proposition that appeals to environmentally aware stakeholders.
Solar Energy Solutions
Solar energy stands out as one of the most accessible and cost-effective renewable energy solutions for businesses. Its versatility and declining costs make it an attractive option for companies seeking sustainable energy alternatives.
Overview of Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity, offering a clean and renewable source of energy for businesses.
Basic Principles of Solar Power
Solar power operates by capturing sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert solar radiation into electricity. This electricity can be used on-site or fed into the grid, providing flexibility and scalability for businesses of all sizes.
Types of Solar Systems
- Photovoltaic (PV) Panels: Convert sunlight directly into electricity and are the most common type of solar system used by businesses.
- Solar Thermal Systems: Use sunlight to generate heat, which can be utilized for heating water or space heating within business premises.
“Solar power has transformed the way businesses approach energy consumption. Its scalability and declining costs make it an ideal choice for companies looking to reduce their carbon footprint without breaking the bank.”
— John Smith, Renewable Energy Consultant
Affordability Factors
The cost of solar technology has decreased significantly over the past decade, making it a more viable option for businesses. Several factors contribute to the affordability of solar energy systems.
Cost Trends and Decreasing Prices of Solar Technology
Advancements in solar technology and increased production scales have led to substantial reductions in the cost of solar panels and installation.
Financing Options: Loans, Leases, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Various financing models enable businesses to adopt solar energy without significant upfront investments:
- Loans: Allow businesses to borrow money to purchase and install solar systems, paying back over time.
- Leases: Enable businesses to lease solar equipment, paying a fixed monthly fee without owning the system.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Allow businesses to purchase the electricity generated by the solar system at a predetermined rate, often lower than grid rates.
Comparison of Solar Financing Options
| Financing Option | Upfront Cost | Ownership | Long-Term Savings | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loans | High | Yes | High | Moderate |
| Leases | Low | No | Moderate | High |
| PPAs | None | No | High | Moderate |
Table 4 compares different solar financing options, helping businesses choose the best model based on their financial situation and long-term goals.
Implementation Considerations for Businesses
Successful implementation of solar energy systems requires careful planning and assessment of various factors.
Assessing Roof Space and Structural Integrity
Before installation, businesses must evaluate their available roof space and ensure that the structure can support the weight of solar panels. Shaded areas and roof orientation also play crucial roles in determining the efficiency of the solar system.
Energy Consumption Analysis and Sizing the System
A thorough analysis of the business’s current and projected energy consumption is essential to determine the appropriate size of the solar system. This ensures that the system can meet the energy needs without over-investment.
Benefits Specific to Solar Energy
Solar energy offers unique advantages that make it particularly beneficial for businesses.
Scalability and Modularity
Solar systems can be easily scaled to match the growth of a business. Companies can start with a smaller installation and expand as their energy needs increase, ensuring flexibility and adaptability.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Once installed, solar energy systems require minimal maintenance, reducing ongoing operational costs. Regular cleaning and periodic inspections are typically sufficient to maintain optimal performance.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world examples of businesses that have successfully adopted solar energy can provide valuable insights and inspiration for others considering the transition.
Example 1: GreenTech Manufacturing
Overview: GreenTech Manufacturing, a mid-sized manufacturing firm, installed a 100 kW solar PV system on its facility roof in 2022.
Cost Savings: The company reduced its annual energy bills by $20,000, achieving a payback period of approximately 7 years.
Operational Benefits: In addition to cost savings, GreenTech Manufacturing experienced increased energy independence and enhanced its reputation as a sustainable business.
Example 2: EcoRetail Chain
Overview: EcoRetail, a nationwide retail chain, implemented solar thermal systems in 50 of its stores to provide hot water for cleaning and other processes.
Cost Savings: The installation led to annual savings of $15,000 per store, totaling $750,000 across all locations.
Operational Benefits: The solar thermal systems reduced reliance on traditional energy sources, contributing to EcoRetail’s commitment to environmental responsibility and attracting eco-conscious customers.
Summary of Case Studies
| Company Name | Solar Solution | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GreenTech Manufacturing | 100 kW PV System | 140,000 | 20,000 | 7 | Increased energy independence, enhanced brand image |
| EcoRetail Chain | Solar Thermal Systems | 300,000 (total) | 750,000 (total) | 4 | Reduced carbon footprint, attracted eco-conscious customers |
Table 5 provides a summary of two case studies, highlighting the financial and operational benefits realized by businesses through solar energy adoption.
Wind Energy Solutions
Wind energy presents a powerful and increasingly affordable renewable option for businesses looking to diversify their energy sources and reduce costs. This section explores the fundamentals of wind energy, its affordability, suitability for various business types, and real-world success stories.

Overview of Wind Energy
Basics of Wind Power Generation
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. This process is facilitated by wind turbines, which convert wind motion into mechanical power, and subsequently transform it into electrical energy through generators. Wind power is a clean, renewable resource that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Types of Wind Turbines Suitable for Businesses
Businesses have several wind turbine options tailored to different scales and energy needs:
- Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs): These are the most common type, featuring blades that rotate on a horizontal axis. They are highly efficient and suitable for larger energy demands.
- Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs): These turbines rotate on a vertical axis, making them ideal for areas with turbulent wind conditions and smaller energy requirements.
- Micro and Small Wind Turbines: Designed for businesses with limited space or lower energy needs, these turbines can be installed on rooftops or small plots of land.
Affordability Factors
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Gains
The initial cost of installing wind turbines can be significant; however, the long-term financial benefits often outweigh these upfront expenses. Businesses can expect substantial savings on energy bills and potential revenue from selling excess energy back to the grid.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Wind Energy Installation
| Turbine Size (kW) | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Energy Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100,000 | 15,000 | 6.7 |
| 100 | 180,000 | 30,000 | 6 |
| 200 | 350,000 | 60,000 | 5.8 |
Table 6 demonstrates the relationship between turbine size, initial investment, annual savings, and payback periods, showcasing the financial viability of wind energy for businesses.
Financing and Leasing Options Tailored for Businesses
To alleviate the burden of high initial costs, various financing and leasing options are available:
- Loans: Businesses can secure loans specifically designed for renewable energy projects, offering favorable interest rates and repayment terms.
- Leases: Leasing wind turbines allows businesses to use the equipment without owning it, typically involving fixed monthly payments.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Under PPAs, businesses agree to purchase the generated electricity at predetermined rates, reducing energy costs without upfront investments.
Wind Energy Financing Options
| Financing Option | Upfront Cost | Ownership | Long-Term Savings | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loans | High | Yes | High | Moderate |
| Leases | Low | No | Moderate | High |
| PPAs | None | No | High | Moderate |
Table 7 compares different financing options for wind energy, helping businesses select the most suitable model based on their financial situation and strategic goals.
Suitable Business Types and Locations
Identifying Businesses with Optimal Wind Conditions
Wind energy is most effective in areas with consistent and strong wind patterns. Businesses located in open plains, coastal regions, or elevated areas are prime candidates for wind energy installations. Conducting a wind resource assessment is essential to determine the feasibility and potential energy output.
Zoning and Permitting Considerations
Before installing wind turbines, businesses must navigate local zoning laws and obtain necessary permits. This process involves:
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensuring that wind installations meet local building codes and environmental regulations.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities to address any concerns and gain support for the project.
- Permitting Process: Securing permits from relevant authorities, which may include environmental impact assessments and safety evaluations.
Benefits Specific to Wind Energy
High Energy Output in Suitable Locations
Wind turbines can generate significant amounts of electricity, especially in areas with favorable wind conditions. This high energy output can meet substantial portions of a business’s energy needs, leading to considerable cost reductions.
Potential for On-Site Generation and Storage
Wind energy systems can be integrated with on-site energy storage solutions, such as batteries, to store excess energy for use during periods of low wind. This enhances energy reliability and ensures a consistent power supply, even when wind conditions are not optimal.
Figure 4: On-Site Wind Energy Generation and Storage
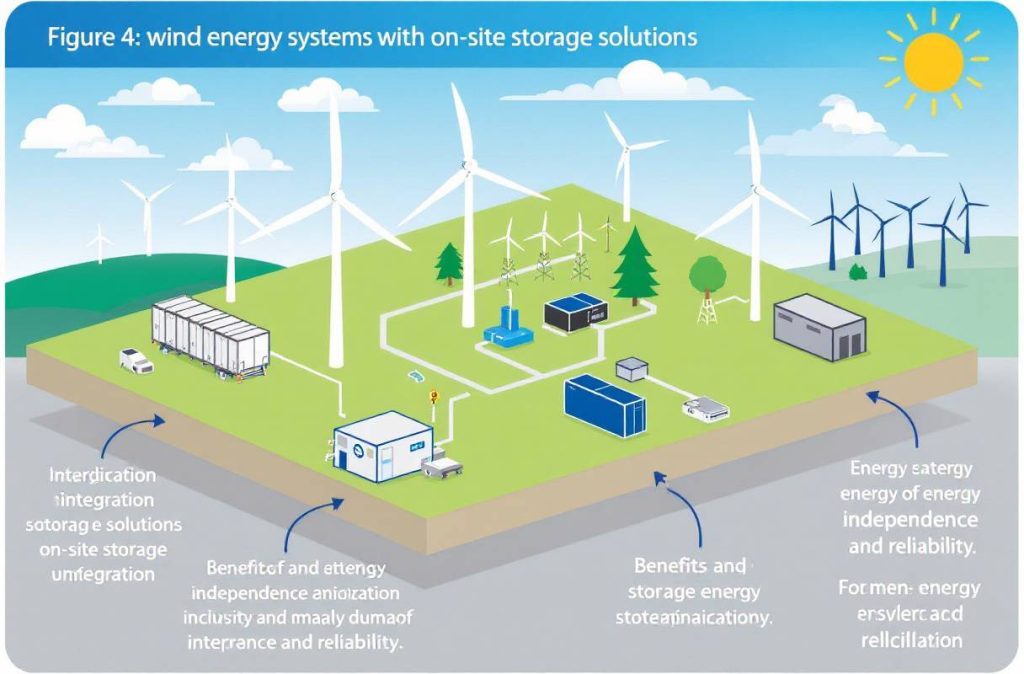
Figure 4 depicts the integration of wind energy systems with on-site storage solutions, highlighting the benefits of energy independence and reliability.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world examples of businesses successfully adopting wind energy can provide valuable insights and inspiration.
Example 1: WindWave Manufacturing
Overview: WindWave Manufacturing, a large-scale manufacturing company, installed a 150 kW horizontal-axis wind turbine on its facility grounds in 2021.
Cost Savings: The company reduced its annual energy bills by $45,000, achieving a payback period of approximately 4 years.
Operational Benefits: WindWave Manufacturing enhanced its energy security and positioned itself as a leader in sustainable manufacturing practices.
Example 2: GreenRetail Stores
Overview: GreenRetail, a chain of retail stores across the Midwest, implemented small vertical-axis wind turbines at 30 locations to supplement their energy needs.
Cost Savings: Each store saved an average of $10,000 annually on energy costs, totaling $300,000 in savings across the chain.
Operational Benefits: The turbines provided reliable energy during peak hours and reduced the stores’ reliance on the grid, contributing to GreenRetail’s sustainability goals.
Summary of Wind Energy Case Studies
| Company Name | Wind Solution | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WindWave Manufacturing | 150 kW HAWT | 270,000 | 45,000 | 6 | Enhanced energy security, sustainability leadership |
| GreenRetail Stores | 30 x VAWTs | 300,000 | 300,000 (total) | 4 | Reduced grid reliance, consistent energy supply |
Table 8 summarizes two case studies, showcasing the financial and operational benefits businesses can achieve through wind energy adoption.
Beyond Solar and Wind: Other Affordable Renewable Options
While solar and wind energy are the most prominent renewable solutions, businesses have access to a variety of other affordable options. This section explores biomass, geothermal, hydropower, energy storage, and hybrid systems, providing a comprehensive overview of alternative renewable energy sources.
Biomass Energy
How Biomass Can Be Utilized by Businesses
Biomass energy involves using organic materials, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, and waste, to generate heat or electricity. Businesses can utilize biomass in several ways:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: These systems generate both electricity and useful heat from biomass, improving overall energy efficiency.
- Biogas Production: Organic waste can be converted into biogas through anaerobic digestion, which can be used for heating, electricity, or as a vehicle fuel.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability Aspects
Biomass is a cost-effective renewable energy source, particularly for businesses with access to organic waste. It not only provides a sustainable energy solution but also helps in waste management and reducing landfill use.
Table 9: Biomass Energy Cost Comparison
| Energy Source | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass CHP | 200,000 | 25,000 | 8 |
| Biogas System | 150,000 | 20,000 | 7.5 |
Table 9 compares the initial investment, annual savings, and payback periods for biomass CHP and biogas systems, highlighting their cost-effectiveness for businesses.
Geothermal Energy
Applications for Heating and Cooling in Commercial Settings
Geothermal energy leverages the stable temperatures beneath the Earth’s surface to provide efficient heating and cooling. Businesses can implement geothermal heat pump systems to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for traditional HVAC systems.
Initial Costs vs. Energy Savings Over Time
Although geothermal installations require a higher initial investment, the long-term energy savings, and low maintenance costs make them a financially viable option for businesses.
Table 10: Geothermal Energy Financials
| System Type | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Energy Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geothermal Heat Pump | 250,000 | 30,000 | 8.3 |
| Geothermal Cooling | 200,000 | 25,000 | 8 |
Table 10 presents the financial aspects of geothermal heat pump and cooling systems, emphasizing their long-term savings potential.
Hydropower Solutions
Small-Scale Hydro Systems for Businesses with Access to Water Sources
Hydropower harnesses the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. Small-scale hydro systems are ideal for businesses located near rivers, streams, or other water sources, providing a reliable and consistent energy supply.
Economic and Environmental Considerations
While small-scale hydropower systems offer significant energy generation potential, businesses must consider environmental impacts, such as water flow disruption, and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Small-Scale Hydropower Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Efficiency | Consistently generates electricity with minimal downtime |
| Low Operating Costs | Minimal maintenance once installed |
| Renewable and Reliable | Provides a steady energy supply from natural water flow |
| Environmental Impact | Requires careful planning to minimize ecological disruption |
Table 11 outlines the key benefits and considerations of small-scale hydropower systems for businesses.
Energy Storage and Hybrid Systems
Importance of Energy Storage in Enhancing Renewable Energy Affordability
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, play a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy. They store excess energy generated during peak production times for use during periods of low generation, ensuring a reliable energy supply.
Combining Multiple Renewable Sources for Optimal Efficiency
Hybrid systems that integrate multiple renewable energy sources (e.g., solar, wind, and biomass) can enhance energy reliability and efficiency. By diversifying energy sources, businesses can mitigate the limitations of individual systems and achieve greater energy independence.
Benefits of Hybrid Renewable Systems
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Reliability | Multiple energy sources reduce dependency on a single source |
| Increased Energy Efficiency | Optimizes energy generation and storage based on demand |
| Cost Savings | Reduces overall energy costs through diversified sources |
| Flexibility | Adapts to varying energy needs and environmental conditions |
Table 12 highlights the advantages of implementing hybrid renewable energy systems, emphasizing their role in improving energy reliability and efficiency.
Comparative Analysis
To assist businesses in selecting the most suitable renewable energy option, a comparative analysis of cost, benefits, and suitability for different business types is essential.
Comparative Analysis of Renewable Energy Options
| Energy Source | Initial Investment ($) | Annual Savings ($) | Payback Period (Years) | Suitable Business Types | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | 75,000 – 270,000 | 10,000 – 40,000 | 6 – 7.5 | Manufacturing, Retail, Offices | Low maintenance, scalable |
| Wind | 100,000 – 350,000 | 15,000 – 60,000 | 5.8 – 7.5 | Manufacturing, Agriculture, Retail | High energy output, energy security |
| Biomass | 150,000 – 200,000 | 20,000 – 25,000 | 7 – 8 | Manufacturing, Food Processing, Waste Management | Waste reduction, sustainable heating |
| Geothermal | 200,000 – 250,000 | 25,000 – 30,000 | 8 – 8.3 | Commercial Buildings, Schools, Hospitals | Efficient heating/cooling, long-term savings |
| Hydropower | 100,000 – 300,000 | 20,000 – 50,000 | 5 – 15 | Businesses near water sources | Reliable energy, high efficiency |
Table 13 provides a comprehensive comparison of various renewable energy options, helping businesses determine the most appropriate solution based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Financing and Incentives for Affordable Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy is not only an environmentally responsible decision but also a financially savvy one. Understanding the various financing options and incentives available can significantly reduce the cost burden for businesses. This section explores the different avenues through which businesses can secure funding and maximize savings when adopting renewable energy solutions.
Government Grants and Subsidies
Overview of Available Federal, State, and Local Programs
Governments at all levels offer a plethora of grants and subsidies to encourage businesses to invest in renewable energy. These programs aim to lower the financial barriers associated with the initial setup costs, making renewable energy more accessible and affordable.
- Federal Programs: The federal government provides substantial support through initiatives like the Renewable Energy Grants and the Business Energy Investment Tax Credit (ITC). These programs offer grants and tax credits to businesses that invest in renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and biomass.
- State Programs: Many states have their own incentives, which can include grants, subsidies, and tax exemptions. For example, California’s Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) offers rebates for the installation of energy storage systems, while New York’s Clean Energy Fund provides financial assistance for renewable energy projects.
- Local Programs: Local municipalities and counties may also offer incentives tailored to the specific needs of their communities. These can include property tax abatements, low-interest loans, and local grants aimed at promoting sustainable energy practices.
Overview of Key Government Grants and Subsidies
| Program Name | Level | Description | Potential Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Grants | Federal | Grants for installing renewable energy systems | Up to 30% |
| Business Energy Investment Tax Credit (ITC) | Federal | Tax credit for a percentage of renewable energy investments | 26% |
| Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) | State (CA) | Rebates for energy storage systems | Up to 50% |
| Clean Energy Fund | State (NY) | Financial assistance for renewable energy projects | Varies by project |
| Local Property Tax Abatements | Local | Reductions in property taxes for renewable installations | Up to 20% |
Table 14 highlights some of the most significant government grants and subsidies available to businesses, illustrating the potential savings they offer.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Processes
Eligibility for these grants and subsidies typically depends on several factors, including the type of business, the size of the renewable energy project, and the specific requirements of the program. Common criteria include:
- Business Size and Revenue: Some programs are targeted towards small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), while others are open to larger corporations.
- Type of Renewable Energy: Eligibility may vary based on whether the business is installing solar panels, wind turbines, biomass systems, or other renewable technologies.
- Project Scope and Location: Certain grants are location-specific or require that the project meets particular environmental or energy-saving criteria.
Application Process Steps for Government Grants
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Programs | Research and identify applicable grants and subsidies |
| 2. Verify Eligibility | Ensure the business meets all eligibility criteria |
| 3. Prepare Documentation | Gather necessary documents such as business financials, project plans, and energy assessments |
| 4. Submit Application | Complete and submit the application through the appropriate channels |
| 5. Follow Up | Monitor application status and provide additional information if required |
| 6. Receive Funding | Upon approval, receive the grant or subsidy as per program guidelines |
Table 15 outlines the typical steps involved in applying for government grants and subsidies, helping businesses navigate the application process efficiently.
Tax Credits and Rebates
Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Other Relevant Credits
Tax credits are a powerful tool for reducing the overall cost of renewable energy installations. The Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is one of the most significant incentives available, offering businesses substantial credit based on the percentage of their renewable energy investment.
- Federal ITC: Currently, the ITC provides a 26% tax credit for businesses investing in solar energy systems. This percentage is set to decrease in the coming years, so early adoption can maximize benefits.
- State-Specific Tax Credits: In addition to federal credits, many states offer their own tax incentives. For example, Massachusetts provides a Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) Program that offers incentives based on the performance of solar installations.
How Businesses Can Maximize Rebates for Renewable Installations
Maximizing rebates involves strategic planning and leveraging multiple incentives simultaneously. Businesses can:
- Combine Federal and State Incentives: Utilize both federal ITC and state-specific rebates to maximize total savings.
- Engage in Energy Efficiency Programs: Some rebates are tied to overall energy efficiency improvements, allowing businesses to secure additional funding.
- Partner with Certified Installers: Working with installers who are familiar with the rebate processes can streamline applications and ensure compliance with all requirements.
Strategies to Maximize Rebates and Tax Credits
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Combine Multiple Incentives | Utilize both federal and state incentives simultaneously |
| Participate in Energy Efficiency Programs | Implement energy-saving measures alongside renewable installations |
| Work with Certified Installers | Ensure compliance and streamline the rebate application process |
| Plan for Future Incentives | Stay informed about upcoming incentive changes to maximize benefits |
Table 16 provides actionable strategies for businesses to maximize their rebates and tax credits, ensuring they receive the highest possible financial benefits from their renewable energy investments.
Leasing and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Advantages of Leasing Solar or Wind Equipment
Leasing renewable energy equipment offers businesses an attractive alternative to purchasing, especially when upfront capital is limited. The primary advantages include:
- Lower Upfront Costs: Leasing typically requires little to no initial investment, allowing businesses to adopt renewable energy without straining their budgets.
- Maintenance and Support: Many leasing agreements include maintenance services, reducing the operational burden on the business.
- Flexibility: Leasing allows businesses to upgrade or scale their renewable energy systems as needed, without being tied to long-term ownership.
Comparison of Leasing vs. Purchasing Renewable Energy Equipment
| Aspect | Leasing | Purchasing |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Low to none | High |
| Ownership | No | Yes |
| Maintenance | Often included | Business responsible |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Long-Term Savings | Moderate | High |
Table 17 compares leasing and purchasing renewable energy equipment, highlighting the benefits of leasing for businesses seeking lower upfront costs and greater flexibility.
Understanding PPAs and Their Financial Implications
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are another financing option where businesses agree to purchase the electricity generated by a renewable energy system at a predetermined rate. Key financial implications include:
- Fixed Energy Rates: PPAs provide predictable energy costs, often lower than current grid rates, helping businesses manage their energy budgets more effectively.
- No Upfront Investment: Similar to leasing, PPAs do not require significant initial capital, making renewable energy accessible without financial strain.
- Potential for Savings: By locking in lower rates, businesses can achieve long-term energy savings, especially as traditional energy prices rise.
Financial Implications of Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Rate | Fixed rate per kWh, often lower than grid rates |
| Upfront Costs | None, typically no initial investment required |
| Contract Length | Typically 10-25 years |
| Long-Term Savings | Potential significant savings as energy prices increase |
| Ownership | Renewable energy provider owns the equipment |
Table 18 outlines the financial aspects of PPAs, demonstrating how businesses can benefit from fixed energy rates and long-term savings without upfront costs.
Green Loans and Financing Options
Specialized Loans for Renewable Energy Projects
Green loans are designed specifically to support environmentally friendly projects, including renewable energy installations. These loans often come with favorable terms such as:
- Lower Interest Rates: Green loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to conventional loans, reducing the overall cost of financing.
- Extended Repayment Periods: Longer repayment terms provide businesses with greater flexibility in managing their finances.
- Tax Benefits: Some green loans may offer additional tax advantages, further enhancing their financial appeal.
Features of Green Loans for Renewable Energy
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Typically lower than standard commercial loans |
| Repayment Terms | Longer repayment periods (10-20 years) |
| Loan Amounts | Vary based on project size and business needs |
| Eligibility Criteria | Projects must meet specific environmental standards |
| Additional Benefits | Potential tax incentives and credits |
Table 19 highlights the key features of green loans, showcasing how they can make renewable energy projects more financially viable for businesses.
Partnering with Financial Institutions that Support Green Initiatives
Partnering with financial institutions that prioritize green initiatives can provide businesses with access to specialized financing options and support services. Benefits include:
- Expertise in Renewable Energy Financing: Financial institutions with a focus on green initiatives understand the unique needs and challenges of renewable energy projects.
- Customized Financing Solutions: These institutions can offer tailored
Top Financial Institutions Supporting Green Initiatives
| Institution Name | Financing Options Offered | Additional Support Services |
|---|---|---|
| Green Bank USA | Green loans, grants, and subsidies | Project consultation and feasibility studies |
| Local Community Banks | Green mortgages and specialized business loans | Financial planning and advisory services |
| International Finance Corp (IFC) | Renewable energy project financing | Technical assistance and capacity building |
| Bank of America | Sustainable business financing | ESG investment support and resources |
| Solar-specific Lenders | Equipment financing and PPAs | Installation and maintenance partnerships |
Table 20 lists some of the leading financial institutions that support green initiatives, providing businesses with a variety of financing options and additional support services.
Implementation Strategies for Businesses
Successfully adopting renewable energy requires careful planning and strategic execution. Implementing the right strategies can ensure a smooth transition, maximize benefits, and achieve long-term sustainability goals. This section outlines the essential steps businesses should take to effectively integrate renewable energy solutions.
Conducting an Energy Audit
Assessing Current Energy Usage and Identifying Opportunities for Savings
An energy audit is the first step in understanding a business’s current energy consumption and identifying areas for improvement. This comprehensive assessment helps businesses pinpoint inefficiencies and prioritize renewable energy investments.
Key Steps in Conducting an Energy Audit:
- Data Collection: Gather information on current energy usage, including utility bills, energy sources, and peak consumption times.
- Site Inspection: Evaluate the physical aspects of the business premises, such as lighting systems, HVAC efficiency, and insulation quality.
- Identify Inefficiencies: Detect areas where energy is being wasted, such as outdated equipment or poor building design.
- Recommendation Report: Develop a detailed report outlining potential energy-saving measures and renewable energy opportunities.
Components of an Energy Audit
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Gathering utility bills, energy consumption records, and equipment specifications |
| Site Inspection | Physical examination of facilities, equipment, and infrastructure |
| Energy Analysis | Evaluating current energy usage patterns and identifying inefficiencies |
| Recommendations | Suggesting energy-saving measures and renewable energy solutions |
| Reporting | Compiling findings and creating a comprehensive audit report |
Table 21 outlines the key components of an energy audit, providing a clear roadmap for businesses to assess their energy usage and identify savings opportunities.
Tools and Resources for Performing Energy Audits
Several tools and resources can assist businesses in conducting effective energy audits:
- Energy Management Software: Platforms like Energy Star Portfolio Manager and RETScreen offer comprehensive tools for tracking and analyzing energy usage.
- Professional Auditors: Hiring certified energy auditors can provide expert insights and detailed assessments tailored to the specific needs of the business.
- Online Resources: Government websites and industry associations often provide guidelines, checklists, and templates to facilitate energy audits.
Developing a Renewable Energy Plan
Setting Realistic Goals and Timelines
A well-structured renewable energy plan outlines clear objectives and realistic timelines for achieving energy sustainability goals. Key elements include:
- Goal Setting: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for renewable energy adoption.
- Timeline Development: Create a phased timeline that outlines when each goal will be achieved, ensuring manageable progress and resource allocation.
- Resource Allocation: Identify the necessary resources, including budget, personnel, and technology, to support the implementation of renewable energy projects.
Example of SMART Goals for Renewable Energy Plan
| Goal | Specific | Measurable | Achievable | Relevant | Time-bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduce energy costs | Decrease electricity bills by 20% | Track monthly energy bills | Invest in solar panels | Aligns with cost-saving objectives | Achieve within 2 years |
| Lower carbon footprint | Reduce CO2 emissions by 30% | Measure emissions annually | Implement wind turbines | Supports sustainability goals | Achieve within 5 years |
| Increase energy independence | Generate 50% of energy on-site | Monitor energy generation metrics | Utilize hybrid systems | Enhances energy security | Achieve within 3 years |
Table 22 provides examples of SMART goals, helping businesses set clear and achievable targets for their renewable energy plans.
Integrating Renewable Energy into Overall Business Strategy
Integrating renewable energy into the broader business strategy ensures that sustainability efforts align with the company’s core objectives and operations. Steps include:
- Leadership Commitment: Secure buy-in from top management to prioritize renewable energy initiatives.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Engage various departments, such as finance, operations, and marketing, to ensure cohesive implementation.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and adjust the renewable energy plan to incorporate new technologies and respond to changing business needs.
Partnering with Renewable Energy Providers
Selecting Reputable Suppliers and Installers
Choosing the right renewable energy providers is crucial for the success of energy projects. Factors to consider include:
- Experience and Expertise: Select providers with a proven track record and extensive experience in renewable energy installations.
- Certifications and Accreditations: Ensure that suppliers and installers hold relevant certifications, such as the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) for solar installers.
- Customer Reviews and References: Evaluate customer testimonials and request references to assess the provider’s reliability and service quality.
Criteria for Selecting Renewable Energy Providers
| Criterion | Description |
|---|---|
| Experience | Years in the industry and number of completed projects |
| Certifications | Relevant industry certifications and accreditations |
| Customer Reviews | Feedback from previous clients and overall satisfaction |
| Warranty and Support | Guarantees offered and availability of ongoing support |
| Pricing and Financing | Competitive pricing and available financing options |
Table 23 outlines the key criteria for selecting reputable renewable energy providers, ensuring businesses choose partners that align with their goals and standards.
Negotiating Contracts and Ensuring Quality Installations
Effective contract negotiation and quality assurance are vital to safeguarding the business’s interests and ensuring successful project outcomes. Key considerations include:
- Clear Terms and Conditions: Define the scope of work, timelines, payment schedules, and responsibilities clearly in the contract.
- Performance Guarantees: Include warranties and performance guarantees to ensure that the renewable energy systems operate as expected.
- Quality Assurance: Implement quality control measures, such as site inspections and performance monitoring, to maintain high standards throughout the installation process.
Key Elements of Renewable Energy Contracts
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Scope of Work | Detailed description of services and deliverables |
| Timeline | Project milestones and completion dates |
| Payment Terms | Payment schedule, including deposits and installment payments |
| Warranties | Guarantees on equipment performance and installation quality |
| Termination Clauses | Conditions under which the contract can be terminated |
Table 24 highlights the essential elements to include in renewable energy contracts, ensuring clarity and protection for both parties.
Monitoring and Maintaining Renewable Energy Systems
Importance of Regular Maintenance for Efficiency and Longevity
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring that renewable energy systems operate efficiently and have a long lifespan. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced performance, higher operating costs, and premature system failure.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance:
- Enhanced Performance: Regular inspections and cleaning keep systems running at optimal efficiency.
- Extended Lifespan: Preventative maintenance reduces wear and tear, prolonging the life of renewable energy equipment.
- Reduced Downtime: Identifying and addressing issues early prevents unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Maintenance Schedule for Renewable Energy Systems
| System Type | Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Cleaning and Inspection | Quarterly | Remove debris and inspect for damage |
| Wind Turbines | Lubrication and Mechanical Check | Biannually | Ensure moving parts are functioning smoothly |
| Biomass Systems | System Performance Review | Monthly | Monitor fuel input and energy output |
| Geothermal Systems | Heat Pump Maintenance | Annually | Check and service heat pumps and connections |
Table 25 provides a sample maintenance schedule for different types of renewable energy systems, emphasizing the importance of regular upkeep.
Utilizing Energy Management Software for Real-Time Monitoring
Energy management software plays a pivotal role in monitoring the performance of renewable energy systems in real time. These tools offer several advantages:
- Real-Time Data Tracking: Monitor energy production, consumption, and system performance in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments and optimizations.
- Predictive Maintenance: Advanced analytics can predict potential issues before they escalate, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generate detailed reports on energy usage, savings, and system performance, facilitating informed decision-making.
Popular Energy Management Software for Businesses
| Software Name | Key Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Star Portfolio Manager | Energy tracking, benchmarking, reporting | Free |
| RETScreen | Renewable energy project analysis, feasibility studies | Free |
| EcoStruxure™ Energy Expert | Real-time monitoring, predictive analytics | Subscription-based |
| Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure | Integrated energy management, IoT integration | Custom pricing |
| Siemens Desigo CC | Building management, energy optimization | Custom pricing |
Table 26 lists some of the most popular energy management software options available to businesses, highlighting their key features and pricing models.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Transitioning to renewable energy can present several challenges for businesses, from managing upfront costs to navigating complex regulations. However, with the right strategies and support, these obstacles can be effectively overcome. This section explores common hurdles businesses face when adopting renewable energy and provides actionable solutions to address them.
Upfront Costs and Budget Constraints
Strategies to Minimize Initial Investment
One of the most significant barriers to adopting renewable energy is the high initial investment required. However, businesses can implement several strategies to reduce these upfront costs:
- Phased Implementation: Start with smaller-scale installations and expand as savings accumulate. This approach spreads out costs over time and allows businesses to adjust based on their financial situation.
- Bulk Purchasing: Partnering with other businesses to purchase renewable energy systems in bulk can lead to significant discounts.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Before investing in renewable energy, optimize existing energy usage to reduce overall demand, thereby lowering the size and cost of the required renewable energy system.
Strategies to Minimize Initial Renewable Energy Investment
| Strategy | Description | Potential Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Phased Implementation | Gradually scale up renewable energy installations | 10-20% |
| Bulk Purchasing | Collaborate with other businesses for bulk discounts | 15-25% |
| Energy Efficiency Upgrades | Improve existing energy systems to reduce overall demand | 20-30% |
| Leveraging Incentives | Utilize grants, tax credits, and rebates to offset costs | 10-40% |
Table 27 outlines effective strategies for minimizing the initial investment required for renewable energy projects, highlighting potential savings.
Leveraging Financing and Incentives to Spread Costs
To alleviate the burden of high upfront costs, businesses can leverage various financing options and incentives:
- Government Grants and Subsidies: As discussed in Section VI, these can cover a significant portion of installation costs.
- Green Loans: Specialized loans offer favorable terms for renewable energy projects, including lower interest rates and extended repayment periods.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): PPAs allow businesses to pay for the energy generated by renewable systems at fixed rates, reducing financial risk.
- Leasing Options: Leasing renewable energy equipment spreads costs over time without the need for large initial capital outlays.
Financing Options to Spread Renewable Energy Costs
| Financing Option | Upfront Cost | Ownership | Long-Term Savings | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government Grants | Low to none | Yes | High | Low |
| Green Loans | Moderate | Yes | High | Moderate |
| Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) | None | No | High | Moderate |
| Leasing | Low | No | Moderate | High |
Table 28 compares various financing options available to businesses, illustrating how each can help spread the costs of renewable energy investments.
Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles
Navigating Local Regulations and Obtaining Necessary Permits
Adhering to local regulations and securing the required permits can be a complex and time-consuming process. Businesses can navigate these hurdles by:
- Understanding Local Laws: Research and comprehend the specific regulations and zoning laws that apply to renewable energy installations in your area.
- Engaging with Authorities: Establish open communication with local regulatory bodies to understand requirements and streamline the permitting process.
- Utilizing Online Resources: Many municipalities offer online portals with detailed guidelines and application procedures for renewable energy projects.
Table 29: Key Steps to Navigate Regulatory and Permitting Processes
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Local Regulations | Identify and understand local zoning laws and energy regulations |
| Engage with Authorities | Communicate with local agencies to clarify requirements |
| Prepare Necessary Documentation | Gather all required documents, including project plans and environmental assessments |
| Submit Applications | Complete and submit permit applications through official channels |
| Follow Up | Monitor application status and respond to any additional requests promptly |
Table 29 outlines the essential steps businesses should take to navigate regulatory and permitting processes effectively.
Working with Consultants or Legal Experts
Collaborating with experts can simplify the regulatory landscape and ensure compliance:
- Hire Renewable Energy Consultants: These professionals can provide valuable insights into the best practices for renewable energy adoption and help navigate the permitting process.
- Engage Legal Experts: Lawyers specializing in energy law can assist with understanding complex regulations and ensuring all legal requirements are met.
- Leverage Industry Associations: Membership in renewable energy associations can provide access to resources and support from experienced professionals.
Benefits of Partnering with Consultants and Legal Experts
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Expertise and Knowledge | Access to specialized knowledge and experience in renewable energy |
| Streamlined Permitting Process | Faster and more efficient navigation of regulatory requirements |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduced risk of non-compliance and associated penalties |
| Time Savings | Allow internal teams to focus on core business operations |
| Enhanced Project Planning | Improved project outcomes through professional guidance |
Table 30 highlights the advantages of partnering with consultants and legal experts, emphasizing how they can help overcome regulatory and permitting challenges.
Technical Expertise and Workforce Training
Ensuring Staff Are Trained to Operate and Maintain New Systems
A successful renewable energy implementation requires skilled personnel to manage and maintain the new systems:
- Training Programs: Invest in training programs to educate staff on the operation and maintenance of renewable energy systems.
- Certifications: Encourage employees to obtain certifications in renewable energy technologies to enhance their expertise.
- Ongoing Education: Provide continuous learning opportunities to keep staff updated on the latest advancements and best practices in renewable energy.
Key Components of Workforce Training for Renewable Energy Systems
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Training | Comprehensive training programs covering system operations and maintenance |
| Certification Programs | Formal certifications to validate employee expertise |
| Ongoing Education | Regular updates and training sessions to keep skills current |
| Hands-On Experience | Practical training through on-site experience and simulations |
| Support Resources | Access to manuals, online courses, and expert consultations |
Table 31 outlines the essential components of effective workforce training programs, ensuring staff are equipped to handle renewable energy systems.
Partnering with Technology Providers for Support
Collaborating with technology providers can provide additional support and ensure the smooth operation of renewable energy systems:
- Vendor Support Services: Utilize the support services offered by renewable energy equipment vendors for troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Technical Assistance: Engage with providers for technical assistance during and after installation to ensure optimal system performance.
- Software Solutions: Implement software solutions provided by technology partners for real-time monitoring and management of energy systems.
Benefits of Partnering with Technology Providers
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Expertise | Access to specialized knowledge and technical support |
| Enhanced System Performance | Improved efficiency and reliability through expert guidance |
| Access to Latest Technologies | Stay updated with the latest advancements and upgrades |
| Comprehensive Support | Ongoing assistance with maintenance and troubleshooting |
| Customized Solutions | Tailored solutions to meet specific business needs |
Table 32 highlights the benefits of partnering with technology providers, emphasizing how these partnerships can enhance system performance and provide essential support.
Managing Energy Supply and Demand
Balancing Renewable Energy Generation with Business Energy Needs
Effectively balancing energy supply and demand is crucial for maximizing the benefits of renewable energy:
- Energy Audits: Conduct regular energy audits to understand usage patterns and identify opportunities for optimization.
- Load Management: Implement load management strategies to shift energy consumption to periods of high renewable energy generation.
- Demand Response Programs: Participate in demand response programs that incentivize businesses to reduce energy usage during peak demand periods.
Strategies for Balancing Energy Supply and Demand
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Energy Audits | Continuously assess energy usage to identify optimization opportunities |
| Load Shifting | Adjust energy consumption patterns to align with renewable energy generation |
| Demand Response Programs | Participate in programs that reward reduced energy usage during peak times |
| Energy Efficiency Measures | Implement measures to reduce overall energy demand |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources with existing energy systems |
Table 33 outlines effective strategies for balancing energy supply and demand, ensuring optimal utilization of renewable energy resources.
Implementing Energy Storage and Smart Grid Solutions
Energy storage and smart grid technologies play a pivotal role in managing energy supply and demand:
- Energy Storage Systems: Utilize batteries and other storage technologies to store excess renewable energy for later use, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
- Smart Grids: Implement smart grid technologies that enable real-time monitoring and management of energy distribution, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine multiple renewable energy sources with energy storage to create a resilient and flexible energy system.
Figure 11: Integration of Energy Storage and Smart Grid Solutions
Figure 11 illustrates how energy storage systems and smart grids work together to optimize energy supply and demand management.
Benefits of Energy Storage and Smart Grid Solutions
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Energy Reliability | Consistent energy supply through stored energy during low generation periods |
| Improved Energy Efficiency | Optimal use of available energy through real-time management |
| Reduced Energy Costs | Lower energy costs by utilizing stored energy during peak pricing |
| Increased System Resilience | Enhanced ability to withstand and recover from energy disruptions |
| Flexibility in Energy Management | Ability to adapt to varying energy needs and renewable energy generation |
*Table 34 highlights the advantages of implementing energy storage and smart grid solutions, emphasizing their role in enhancing energy reliability and efficiency.*
Future Trends in Affordable Renewable Energy for Businesses
The renewable energy landscape is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements, market dynamics, and global sustainability goals. Understanding future trends can help businesses stay ahead and make informed decisions about their renewable energy strategies.
Technological Advancements
Innovations Reducing Costs and Increasing Efficiency
Technological innovations are pivotal in making renewable energy more affordable and efficient for businesses:
- Advanced Photovoltaic (PV) Technologies: Improvements in solar panel efficiency and durability are reducing the cost per watt of solar energy.
- Wind Turbine Innovations: Enhanced turbine designs and materials are increasing energy output and lowering maintenance costs.
- Energy Storage Breakthroughs: Advances in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, are providing higher energy densities and longer lifespans at lower costs.
- Smart Energy Management Systems: AI and machine learning are being integrated into energy management systems to optimize energy usage and predict maintenance needs.
Key Technological Advancements in Renewable Energy
| Technology | Innovation Description | Impact on Cost and Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced PV Panels | Higher efficiency and durability materials | Lower cost per watt, increased energy output |
| Next-Gen Wind Turbines | Improved blade designs and materials | Higher energy production, reduced maintenance costs |
| Solid-State Batteries | Higher energy density and longer lifespan | Reduced storage costs, increased reliability |
| AI-Powered Energy Management | AI algorithms optimizing energy usage and maintenance | Enhanced efficiency, predictive maintenance |
Table 35 outlines significant technological advancements in renewable energy, highlighting their impact on reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Emerging Renewable Technologies on the Horizon
Several emerging technologies hold the promise of further transforming the renewable energy landscape:
- Floating Solar Farms: Solar panels mounted on floating platforms can maximize land use and reduce water evaporation in reservoirs.
- Offshore Wind Energy: Advances in offshore wind turbine technology are making it possible to harness stronger and more consistent wind resources.
- Green Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced using renewable energy can serve as a clean fuel for various industrial applications, offering a versatile energy storage solution.
- Perovskite Solar Cells: These next-generation solar cells offer higher efficiency and lower production costs compared to traditional silicon-based panels.
Potential Impact of Emerging Renewable Technologies
| Emerging Technology | Potential Applications | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Floating Solar Farms | Large-scale solar installations on water bodies | Maximized land use, reduced water evaporation |
| Offshore Wind Energy | Wind energy generation in coastal and offshore areas | Access to stronger and more consistent winds |
| Green Hydrogen | Industrial fuel, energy storage, transportation | Versatile clean energy carrier, decarbonization of hard-to-electrify sectors |
| Perovskite Solar Cells | High-efficiency solar panels for commercial use | Lower production costs, higher energy efficiency |
Table 36 highlights the potential applications and benefits of emerging renewable energy technologies, emphasizing their role in future energy solutions.
Market Trends and Predictions
Forecasting the Growth of Renewable Energy Adoption in the Business Sector
The adoption of renewable energy in the business sector is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by decreasing costs, technological advancements, and increasing regulatory support:
- Increased Investment: Businesses are projected to increase their investments in renewable energy, with renewable energy assets expected to surpass fossil fuels in new installations.
- Corporate Renewable Targets: More companies are setting ambitious renewable energy targets, aligning with global sustainability goals and enhancing their corporate responsibility profiles.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: The shift towards decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids and on-site renewable installations, is expected to grow, providing businesses with greater energy independence and resilience.
Renewable Energy Adoption Growth Projections
| Year | Projected Renewable Energy Investment (USD Billion) | Projected Renewable Energy Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 500 | 1,200 |
| 2025 | 550 | 1,350 |
| 2030 | 800 | 2,000 |
| 2035 | 1,000 | 2,500 |
Table 37 provides projections for renewable energy investments and capacity growth over the next decade, illustrating the expected expansion of renewable energy adoption in the business sector.
Impact of Global Policies and Climate Goals on Renewable Energy
Global policies and climate goals are significantly influencing the renewable energy market:
- Paris Agreement: Commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are driving businesses to adopt renewable energy to meet regulatory requirements and avoid carbon penalties.
- National Renewable Energy Targets: Countries are setting specific renewable energy targets, providing a clear framework and incentives for businesses to invest in renewable technologies.
- Carbon Pricing and Trading: Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms and trading schemes encourages businesses to lower their carbon footprint by adopting cleaner energy sources.
Table 38: Influence of Global Policies on Renewable Energy Adoption
| Policy/Agreement | Description | Impact on Renewable Energy Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Paris Agreement | International treaty to limit global warming | Increased business investments in renewable energy to meet emission targets |
| National Renewable Targets | Specific national goals for renewable energy capacity | Enhanced incentives and support for businesses adopting renewables |
| Carbon Pricing and Trading | Economic mechanisms to price carbon emissions | Financial incentives for reducing carbon footprint through renewable energy adoption |
| Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) | Regulations requiring a certain percentage of energy from renewables | Guaranteed market demand for renewable energy sources |
Table 38 illustrates how various global policies and agreements are driving renewable energy adoption, highlighting their impact on business investments and strategies.
Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
Increasing Importance of Sustainability in Business Operations
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, influencing everything from supply chain management to corporate governance:
- Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly favoring businesses that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, driving companies to adopt renewable energy to meet these expectations.
- Investor Preferences: Investors are prioritizing sustainable and environmentally responsible companies, encouraging businesses to integrate renewable energy into their operations to attract investment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to sustainability standards and regulations is becoming essential for maintaining business licenses and avoiding legal repercussions.
Drivers of Sustainability in Business Operations
| Driver | Description |
|---|---|
| Consumer Demand | Preference for eco-friendly products and services |
| Investor Preferences | Focus on sustainable and responsible investments |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to environmental laws and sustainability standards |
| Competitive Advantage | Differentiation through sustainability initiatives |
| Brand Reputation | Enhanced reputation through commitment to sustainability |
Table 39 outlines the key drivers pushing businesses towards greater sustainability, emphasizing the role of renewable energy in meeting these drivers.
How Renewable Energy Contributes to Broader Corporate Responsibility Initiatives
Adopting renewable energy is a significant aspect of broader corporate responsibility (CR) initiatives, contributing to various sustainability goals:
- Carbon Neutrality: Renewable energy adoption is a critical step towards achieving carbon neutrality, helping businesses offset their greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable Supply Chains: Integrating renewable energy into operations supports sustainable supply chain practices by reducing overall environmental impact.
- Community Engagement: Businesses that invest in renewable energy often engage with local communities through green initiatives, fostering positive relationships and social responsibility.
- Employee Engagement: Sustainable practices, including the adoption of renewable energy, can enhance employee morale and attract talent who prioritize working for environmentally responsible companies.
Contributions of Renewable Energy to Corporate Responsibility
| Corporate Responsibility Initiative | Contribution of Renewable Energy |
|---|---|
| Carbon Neutrality | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and offsets carbon footprint |
| Sustainable Supply Chains | Lowers environmental impact of production and operations |
| Community Engagement | Supports local sustainability projects and creates positive community impact |
| Employee Engagement | Enhances workplace sustainability culture and attracts eco-conscious talent |
| Ethical Business Practices | Demonstrates commitment to environmental stewardship and responsible resource management |
Table 40 highlights how renewable energy adoption supports various corporate responsibility initiatives, reinforcing a company’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored a range of affordable renewable energy solutions tailored for businesses, including solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, and hydropower. Each of these options offers unique benefits and cost-saving opportunities that make renewable energy a feasible and advantageous choice for businesses of all sizes.
- Solar Energy: Highly scalable and low-maintenance, solar power is one of the most accessible renewable energy options.
- Wind Energy: With high energy output and energy independence benefits, wind energy is ideal for businesses located in windy regions.
- Biomass and Geothermal: These options provide sustainable heating and power solutions, particularly suitable for industries with specific energy needs.
- Hydropower: Small-scale hydro systems offer reliable and efficient energy generation for businesses with access to water sources.
- Energy Storage and Smart Grids: These technologies enhance the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy systems, ensuring consistent energy supply.
Now is the perfect time for businesses to take the first steps towards adopting renewable energy. By leveraging the strategies, financing options, and incentives discussed in this article, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and sustainability commitments.
Next Steps for Interested Businesses:
- Conduct an Energy Audit: Assess your current energy usage to identify opportunities for improvement and renewable energy adoption.
- Explore Financing Options: Research and apply for government grants, and green loans, or consider leasing and PPAs to finance your renewable energy projects.
- Develop a Renewable Energy Plan: Set clear, achievable goals and integrate renewable energy into your overall business strategy.
- Partner with Reputable Providers: Select experienced suppliers and installers to ensure high-quality installations and ongoing support.
- Monitor and Optimize: Implement energy management software to track performance and maintain your renewable energy systems for maximum efficiency and longevity.
Final Thoughts
Investing in renewable energy is not just a responsible choice for the planet—it’s a strategic business decision that offers long-term financial and operational benefits. As businesses continue to navigate an ever-changing economic landscape, renewable energy provides a pathway to resilience, sustainability, and competitive advantage.
By embracing renewable energy, businesses play a crucial role in fostering a sustainable future, driving innovation, and setting industry standards for environmental stewardship.
FAQs
1. What are the most affordable renewable energy options for businesses?
Solar and wind energy are typically the most cost-effective renewable options for businesses. Advances in technology and decreasing installation costs have made these solutions increasingly accessible and affordable.
2. How can businesses finance renewable energy projects on a tight budget?
Businesses can finance renewable energy projects through government grants, tax credits, green loans, leasing options, and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). These options help spread out costs and reduce the initial financial burden.
3. What incentives are available for businesses adopting renewable energy?
Incentives include federal and state grants, tax credits like the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), rebates from utilities, and Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs). These incentives can significantly lower the cost of renewable energy installations.
4. How do renewable energy systems benefit a business’s bottom line?
Renewable energy systems reduce energy bills, provide protection against energy price volatility, and can increase property value. Over time, the initial investment is often offset by substantial long-term savings.
5. What steps should a business take to implement renewable energy solutions?
Businesses should start by conducting an energy audit, developing a renewable energy plan, exploring financing options, partnering with reputable energy providers, and implementing energy management systems for ongoing optimization.
Additional Resources
Useful Links and References
Government Websites for Incentives and Grants:
Industry Associations and Renewable Energy Organizations:
Energy Savings Calculator
Energy Management Software Providers:
By following this comprehensive guide, businesses can navigate the landscape of affordable renewable energy solutions, making informed decisions that benefit both their bottom line and the environment.