The buzz around Tesla potentially entering the e-bike market has sparked intrigue and speculation among tech enthusiasts, cyclists, and environmentalists alike. This anticipated move could disrupt the e-bike industry much like Tesla’s impact on electric vehicles, bringing advanced technology and innovative design to the forefront of personal transportation.
Tesla has been a trailblazer in the electric vehicle (EV) sector, revolutionizing how the world perceives sustainable transportation. With groundbreaking developments in battery technology, autonomous driving, and renewable energy integration, Tesla has set new standards for performance and efficiency.
The company’s influence extends beyond automobiles; its commitment to reducing carbon emissions and promoting clean energy solutions has accelerated global interest in sustainable living.
Meanwhile, traditional e-bikes have experienced a surge in popularity over the past decade. E-bikes have become a staple in urban commuting and recreational cycling, offering an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to conventional vehicles.
Brands like Bosch, Specialized, and Giant have dominated the market, providing reliable models that cater to a wide range of riders. Despite their success, there remains room for innovation, particularly in battery longevity, smart technology integration, and design aesthetics.
This article aims to compare the hypothetical Tesla Bike with existing traditional e-bikes, analyzing potential impacts on the industry. By exploring how Tesla’s entry could revolutionize the e-bike market through advanced technology, cutting-edge design, and unparalleled innovation, we delve into what the future might hold for personal electric transportation.
Overview of Traditional E-Bikes
E-bikes, or electric bicycles, have transformed the way people commute and enjoy cycling by combining traditional pedal power with electric assistance. Understanding the basics of traditional e-bikes sets the stage for comparing them with the speculative Tesla Bike.
Definition and Categories
- Pedal-Assist E-Bikes (Pedelecs):
- These bikes provide electric assistance only when the rider is pedaling.
- The motor amplifies the rider’s input, making it easier to climb hills or ride against the wind.
- Assistance typically cuts off at speeds above 20 mph to comply with regulations.
- Throttle-Controlled E-Bikes:
- These e-bikes allow riders to engage the motor with a throttle, providing power without the need to pedal.
- Ideal for riders who want the option to rest their legs while still moving.
- May be subject to stricter regulations due to their capability to function like a moped.
Market Leaders and Models
Several brands have established themselves as leaders in the e-bike industry:
- Bosch:
- Known for their reliable motors and battery systems used by various bike manufacturers.
- Notable Model: Bosch Performance Line CX system, favored for mountain e-bikes.
- Specialized:
- Offers a range of high-quality e-bikes with integrated technology.
- Notable Model: Turbo Vado, designed for urban commuting with a sleek design.
- Giant:
- One of the world’s largest bicycle manufacturers, offering diverse e-bike options.
- Notable Model: Giant Explore E+, versatile for both city streets and light trails.
Standard Features
- Battery Life:
- Traditional e-bikes typically offer an average range of 40-60 miles per charge, depending on factors like terrain, rider weight, and level of assistance.
- Motor Power:
- Commonly equipped with motors ranging from 250W to 500W, balancing sufficient assistance with legal power limits.
- Design Elements:
- Functional designs that often resemble traditional bicycles.
- Emphasis on comfort and practicality rather than futuristic aesthetics.
Limitations
While traditional e-bikes have advanced significantly, they still face some limitations:
- Longer Charging Times:
- Charging can take anywhere from 3 to 6 hours, which may be inconvenient for frequent riders.
- Limited Smart Technology Integration:
- Basic onboard computers provide essential information, but advanced connectivity features are less common.
- Weight and Bulkiness:
- E-bikes can be heavy due to batteries and motors, often weighing between 45 to 60 pounds, affecting portability and handling.
Comparison of Standard Traditional E-Bike Features
| Feature | Typical Specification |
|---|---|
| Battery Range | 40-60 miles per charge |
| Motor Power | 250W – 500W |
| Charging Time | 3 – 6 hours |
| Weight | 45 – 60 pounds |
| Maximum Speed | 20 – 28 mph (depending on class) |
| Connectivity Features | Basic (e.g., LCD display) |
Introducing the Tesla Bike
The concept of a Tesla Bike has generated excitement, imagining how Tesla’s expertise in electric vehicles could translate to the e-bike industry. While purely speculative, envisioning the Tesla Bike allows us to explore its potential impact.
Speculative Design and Innovation
Futuristic Aesthetics:
- Sleek Lines and Minimalist Design:
- A signature Tesla approach, combining elegance with functionality.
- Clean frame with integrated components to reduce clutter.
- High-Quality Materials:
- Use of lightweight yet strong materials like carbon fiber or aerospace-grade aluminum to enhance performance and durability.
- Aerodynamic Features:
- Streamlined shapes to reduce air resistance, improving efficiency and speed.
Anticipated Technical Specifications
Advanced Battery Technology:
- Extended Range:
- Leveraging Tesla’s industry-leading battery technology to achieve up to 100 miles on a single charge.
- Rapid Charging Capabilities:
- Potential to charge fully in 1-2 hours, minimizing downtime.
Motor Power:
- High-Torque Motors:
- Providing swift acceleration and improved hill-climbing capabilities.
- Possibly exceeding the standard 250W – 500W while complying with legal limits through intelligent power management.
- Charging Compatibility:
- Integration with Tesla Charging Infrastructure:
- The ability to charge using Tesla home chargers enhances convenience for existing Tesla customers.
- Integration with Tesla Charging Infrastructure:
Speculative Tesla Bike Specifications vs. Traditional E-Bikes
| Feature | Tesla Bike | Traditional E-Bikes |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Range | Up to 100 miles | 40-60 miles |
| Charging Time | Approximately 1-2 hours | 3 – 6 hours |
| Motor Power | High-torque motor | 250W – 500W |
| Weight | Estimated 35-45 pounds | 45 – 60 pounds |
| Connectivity | Advanced smart features | Basic displays |
Innovative Features
Smart Connectivity:
- Tesla App Integration:
- Real-time diagnostics, over-the-air updates, and customization options are accessible via smartphone.
- IoT and AI Integration:
- Learning rider habits to optimize performance and energy efficiency.
Autonomous Capabilities:
- Self-Balancing Technology:
- Gyroscopic systems assist with stability, particularly at low speeds.
- Automated Braking and Assistance:
- Sensors detect obstacles with automatic braking to prevent collisions.
Safety Enhancements:
- Collision Detection:
- Advanced sensor arrays to monitor surroundings and alert the rider of potential hazards.
- Adaptive Lighting:
- LED lights that adjust brightness based on ambient conditions and speed.
- Advanced Sensor Systems:
- Integration of radar and cameras for comprehensive environmental awareness.
Envisioning the Tesla Bike Experience
The Tesla Bike could redefine user interaction with e-bikes:
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Touchscreen displays integrated into the handlebars, providing navigation, battery status, and performance metrics.
- Seamless Ecosystem Integration:
- Syncing with other Tesla products, such as cars and home energy systems, for a unified user experience.
- Sustainability Focus:
- Emphasis on eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes aligns with Tesla’s commitment to sustainability.
Potential Impact on the E-Bike Industry
- Setting New Standards:
- The Tesla Bike could push competitors to innovate, leading to overall advancements in the e-bike market.
- Consumer Expectations:
- Riders may begin to expect longer ranges, faster charging, and smarter technology as standard features.
- Market Expansion:
- Tesla’s brand recognition could attract new demographics to e-biking, expanding the market.
By juxtaposing the speculative Tesla Bike against traditional e-bikes, we can appreciate the potential advancements Tesla could bring to the industry. While traditional e-bikes offer reliable and efficient transportation, Tesla’s entry could catalyze significant innovation, ultimately benefiting consumers and the environment.
Comparative Analysis
When examining the potential impact of the Tesla Bike compared to traditional e-bikes, several key factors emerge that highlight Tesla’s ability to revolutionize the industry. This comparative analysis focuses on performance metrics, technological advancements, design aesthetics, and user experience.
Performance Metrics
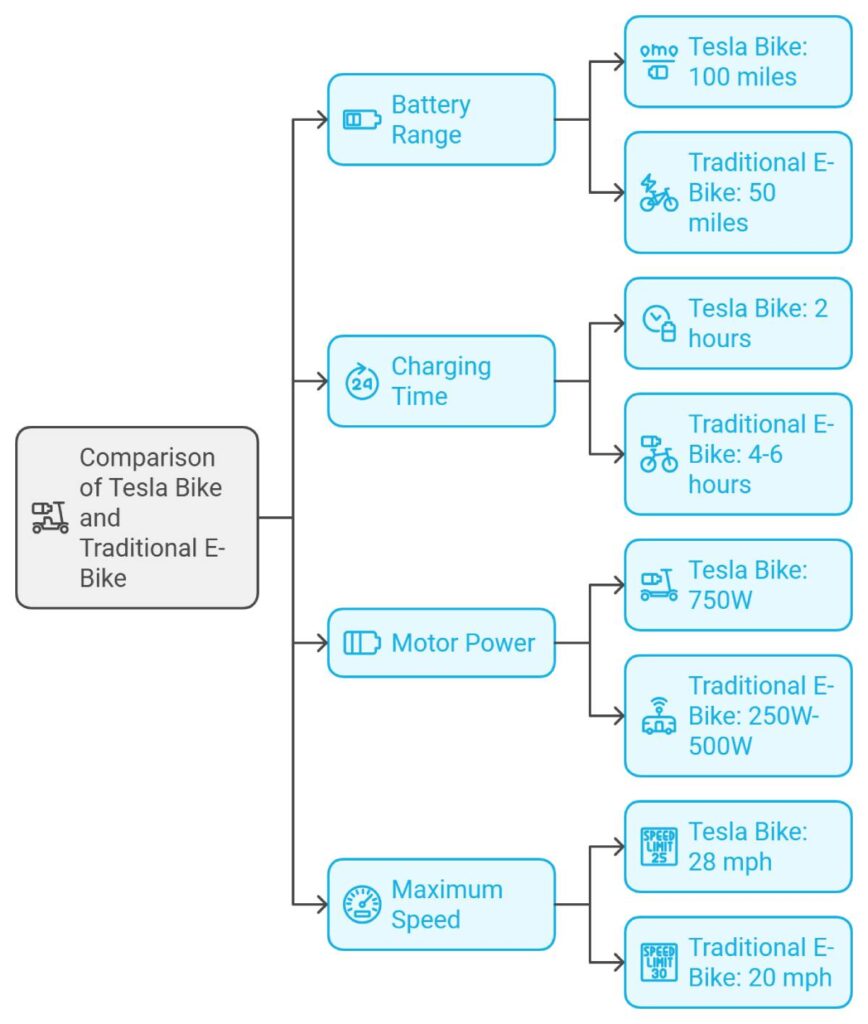
A side-by-side comparison of the Tesla Bike’s anticipated specifications versus traditional e-bikes illustrates significant differences in performance.
| Feature | Tesla Bike | Traditional E-Bikes |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Range | Up to 100 miles | 40-60 miles |
| Charging Time | Approximately 1-2 hours | 3-6 hours |
| Motor Power | High-torque motor | 250W – 500W |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 28 mph | Up to 20-28 mph |
- Battery Range: The Tesla Bike is expected to offer an impressive range of up to 100 miles on a single charge, significantly outperforming traditional e-bikes, which typically provide 40-60 miles. This extended range would make long-distance commuting and recreational riding more feasible without frequent recharging.
- Charging Time: With rapid charging capabilities, the Tesla Bike could recharge in approximately 1-2 hours, compared to the 3-6 hours often required for traditional e-bikes. This efficiency enhances convenience for daily use and reduces downtime.
- Motor Power: Equipped with a high-torque motor, the Tesla Bike would deliver superior acceleration and hill-climbing ability. Traditional e-bikes usually feature motors ranging from 250W to 500W, which are adequate but may lack the power for more demanding rides.
- Maximum Speed: Both the Tesla Bike and traditional e-bikes comply with regulatory speed limits, typically capping at 28 mph. However, Tesla’s engineering could provide smoother acceleration and more efficient speed regulation.
“If Tesla brings their battery technology to e-bikes, we could see ranges and charging times that outpace anything currently available.”
— Alex Martinez, E-Bike Industry Analyst
Technological Advancements
Tesla Bike:
- AI Integration: Incorporating artificial intelligence to learn rider habits, optimize performance, and provide predictive maintenance alerts.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Ability to receive software updates that enhance functionality, security, and user experience without requiring physical modifications.
- IoT Connectivity: Seamless integration with smart devices and infrastructure, enabling features like remote diagnostics, ride customization, and connectivity with other Tesla products.
Traditional E-Bikes:
- Basic Pedal-Assist: Standard assistance based on rider input without adaptive learning capabilities.
- Limited Smart Features: May include basic displays showing speed, distance, and battery life, but lack advanced connectivity or personalization.
“Integrating AI and IoT into an e-bike could revolutionize how we interact with our bikes, making the ride more personalized and efficient.”
— Samantha Lee, Professional Cyclist
Design and Aesthetics
Tesla Bike:
- Modern and Aerodynamic Design: Sleek lines and a minimalist approach reflect Tesla’s signature aesthetic, prioritizing both form and function.
- Premium Materials: Use of high-quality materials like carbon fiber or aerospace-grade aluminum to reduce weight and increase durability.
- Integrated Components: Concealed wiring, built-in lighting, and seamless integration of electronic components for a clean look.
Traditional E-Bikes:
- Varied Designs: While some brands offer modern designs, many traditional e-bikes maintain a conventional bicycle appearance.
- Standard Materials: Common use of aluminum or steel frames, which may add weight and lack the premium feel.
- Exposed Components: Visible wiring and add-on components can detract from the overall aesthetic.
User Experience
Tesla Bike:
- Personalization: Riders can customize settings such as power output, ride modes, and display preferences through an intuitive interface.
- Intuitive Interfaces: Touchscreen displays and smartphone integration offer easy access to information and controls.
- Ecosystem Integration: Compatibility with other Tesla products enhances functionality, such as syncing with a Tesla vehicle for route planning or using home energy solutions for charging.
Traditional E-Bikes:
- Basic Controls: Simple interfaces with limited customization options.
- Standalone Products: Generally do not integrate with other devices or ecosystems, offering a more isolated experience.
Impact on the E-Bike Market
The introduction of the Tesla Bike could have profound effects on the e-bike industry, influencing market dynamics, consumer expectations, and competitive strategies.
Market Disruption
- Setting New Industry Standards: Tesla’s advanced technology and innovative features may redefine what consumers expect from an e-bike, compelling competitors to elevate their offerings.
- Innovation Pressure: Established e-bike manufacturers might face increased pressure to invest in research and development to keep pace with Tesla’s technological advancements.
- Market Expansion: Tesla’s brand recognition could attract new customers to the e-bike market, expanding its overall size and potential.
Consumer Expectations
- Enhanced Performance: With superior battery life and motor power, consumers may begin to expect longer ranges and more robust performance as standard.
- Smart Features: Integration of AI, IoT, and over-the-air updates could shift consumer demand towards e-bikes with advanced connectivity and personalization.
- Aesthetic Appeal: A focus on sleek, modern design may lead consumers to prioritize aesthetics alongside functionality in their purchasing decisions.
Pricing Strategies
| Category | Tesla Bike | Traditional E-Bikes |
|---|---|---|
| Price Range | Expected premium pricing ($5,000 – $7,000) | Wide range ($1,000 – $5,000) |
| Features | Advanced technology, superior performance, premium design | Basic to mid-range features, varying quality |
- Tesla Bike: The expected premium pricing reflects the value added through advanced technology and design. Financing options or subscription models may be offered to make the bike more accessible.
- Traditional E-Bikes: Generally more affordable, catering to budget-conscious consumers. However, they may lack the advanced features and performance of the Tesla Bike.
Competitive Landscape
- Pressure on Competitors: Traditional e-bike manufacturers may need to innovate rapidly to retain market share, potentially leading to collaborations or shifts in business models.
- Diversification: Companies might diversify their product lines, offering both affordable models and high-end options with improved features.
- Market Segmentation: The e-bike market could become more segmented, with clear distinctions between premium, technology-driven bikes, and more basic, cost-effective models.
Consumer Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Greater Choice: Consumers will have access to a wider range of e-bike options tailored to different needs and preferences.
- Technological Advancements: Enhanced features may improve safety, convenience, and overall riding experience.
Challenges:
- Higher Costs: Premium features come at a higher price, which may be a barrier for some consumers.
- Learning Curve: Advanced technology may require users to adapt to new interfaces and functionalities.
The Tesla Bike’s potential entry into the market represents a significant shift that could redefine the standards for e-bikes. By offering superior performance, cutting-edge technology, and sophisticated design, Tesla could not only capture a significant market share but also drive the entire industry toward innovation and improved consumer experiences.
Please note that the Tesla Bike is a speculative concept. The above analysis is based on the potential features and impacts of Tesla entering the e-bike market.
Potential Challenges
Regulatory Considerations: Navigating E-Bike Laws and Compliance
The introduction of the Tesla Bike into the global market would require careful navigation of varying e-bike regulations across different countries and regions. Compliance with laws regarding speed limits, power output, and vehicle classification is crucial to ensure widespread acceptance and avoid legal hurdles.
- Speed and Power Limits: Many countries have strict regulations on the maximum speed and motor power of e-bikes. For instance:
- European Union: Limits e-bikes to a maximum continuous rated power of 250W and assistance up to 25 km/h (approximately 15.5 mph).
- United States: Allows higher power outputs, with Class 1 and Class 2 e-bikes limited to 20 mph and Class 3 e-bikes up to 28 mph, typically with a maximum power of 750W.
- Classification Challenges: Advanced features like high-torque motors and autonomous capabilities might blur the lines between e-bikes and motorcycles or mopeds, leading to stricter regulations, licensing requirements, and potential mandatory insurance.
- Safety Standards Compliance: Adherence to international safety standards such as EN 15194 in Europe or UL 2849 in North America is essential. This includes rigorous testing for electrical, mechanical, and fire safety to ensure the bike meets all regulatory requirements.
Market Adoption: Convincing Traditional Cyclists to Embrace High-Tech Options
While the Tesla Bike’s innovative features could attract tech enthusiasts, convincing traditional cyclists and the general public to adopt this high-tech option presents its own set of challenges.
- Technological Learning Curve: Advanced features like AI integration and autonomous capabilities may intimidate some users. Tesla would need to prioritize user-friendly interfaces and provide educational resources to ease the transition.
- Cost Considerations: The expected premium pricing could be a barrier for many potential buyers. Traditional e-bikes are available at various price points, often starting as low as $1,000, whereas the Tesla Bike might range between $5,000 to $7,000. E-Bike Type Price Range (USD) Entry-Level E-Bikes $1,000 – $2,000 Mid-Range E-Bikes $2,000 – $4,000 High-End E-Bikes $4,000 – $6,000 Tesla Bike (Speculative) $5,000 – $7,000
- Cultural Resistance: Some cyclists prefer the simplicity and mechanical reliability of traditional bicycles. Overcoming this mindset requires highlighting the tangible benefits of the Tesla Bike, such as improved efficiency, environmental impact, and enhanced riding experience.
Infrastructure Needs: Establishing Support Systems
The successful adoption of the Tesla Bike depends not only on the product itself but also on the supporting infrastructure.
- Charging Availability: While home charging is convenient, the lack of public e-bike charging stations could limit long-distance travel. Tesla might need to invest in expanding charging infrastructure or adapt existing Tesla Superchargers to accommodate e-bikes.
- Maintenance and Service Networks: Advanced technology requires specialized maintenance. Establishing a network of service centers with trained technicians is crucial to provide timely support and build consumer trust.
- Software Support: Reliance on software and connectivity means consistent updates and cybersecurity measures are essential. Ensuring robust digital infrastructure to support over-the-air updates and data security is vital for user confidence.
The Future of E-Biking
Technological Trends: Embracing AI and Connectivity
The e-bike industry is poised for significant advancements, with technology playing a central role in its evolution.
- Growth of AI and Machine Learning: Incorporating AI can enhance personalization, optimize battery management, and improve safety features. The Tesla Bike’s potential AI integration could set a new benchmark in the industry.
- Connectivity and IoT Integration: Smart connectivity allows for features like real-time diagnostics, GPS navigation, and integration with other smart devices. This interconnectedness enhances the user experience and aligns with the trend towards smart cities.
- Advanced Materials and Manufacturing: Innovations in materials science could lead to lighter, stronger bike frames, improving performance and efficiency.
Environmental Impact: Promoting Sustainable Transportation
E-bikes are increasingly recognized for their environmental benefits, contributing to global efforts to reduce pollution and combat climate change.
- Reducing Urban Pollution: By offering a zero-emission mode of transport, e-bikes help decrease air pollution in congested cities. According to the European Cyclists’ Federation, e-bikes emit approximately 21 grams of CO2 per passenger-kilometer, significantly less than cars. Transport Mode CO2 Emissions (g/passenger-km) Car (Petrol) 271 Bus 101 Traditional Bicycle 16 E-Bike 21
- Encouraging Active Mobility: E-bikes make cycling accessible to a broader audience, promoting healthier lifestyles and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Charging e-bikes with renewable energy sources amplifies their environmental benefits. Tesla’s expertise in solar energy and battery storage could facilitate this integration.
Tesla’s Influence: Driving Innovation and Sustainability
Tesla’s potential entry into the e-bike market could accelerate innovation and set new industry standards.
- Catalyzing Competitors: Tesla’s reputation for disruption may prompt other manufacturers to innovate, leading to overall industry advancement.
- Elevating Consumer Expectations: By introducing advanced features, Tesla could raise the bar for what consumers expect from e-bikes, encouraging a shift towards smarter, more efficient models.
- Advocacy for Sustainable Policies: Tesla’s influence might extend to advocating for supportive policies and infrastructure development, benefiting the entire e-bike ecosystem.
Consumer Empowerment: Enhancing Personal Mobility
The Tesla Bike represents a leap forward in giving consumers greater control over their transportation choices.
- Personalization and Control: Advanced settings allow riders to customize performance, from adjusting power assistance levels to selecting ride modes tailored to different conditions.
- Data-Driven Insights: Access to ride analytics and health metrics empowers users to track their fitness progress and optimize their commuting habits.
- Integration with Daily Life: Seamless connectivity with smartphones and other devices enhances convenience, allowing features like remote locking, theft tracking, and synchronization with personal calendars for optimized route planning.
By addressing these potential challenges and embracing future technological trends, the Tesla Bike could play a pivotal role in shaping the future of e-biking. Its success would not only depend on its innovative features but also on Tesla’s ability to navigate regulatory landscapes, foster market adoption, and build the necessary infrastructure to support its advanced technology.
As the industry evolves, the Tesla Bike symbolizes the transformative potential of integrating cutting-edge technology with sustainable transportation solutions.
Conclusion
As we explore the potential of the Tesla Bike compared to traditional e-bikes, several key differences and advantages emerge that could significantly impact the future of personal transportation.
The Tesla Bike stands out with its advanced technology, featuring AI integration, over-the-air updates, and IoT connectivity, offering a level of personalization and performance optimization not commonly found in traditional e-bikes.
Its superior battery range of up to 100 miles and rapid charging capabilities (approximately 1-2 hours) surpass the average 40-60 miles range and 3-6 hours charging time of conventional models.
The high-torque motor promises better acceleration and hill-climbing ability, while the sleek, aerodynamic design using premium materials enhances both aesthetics and functionality.
Traditional e-bikes, while reliable and more accessible in terms of pricing, often lack these cutting-edge features. They typically offer basic pedal-assist functionality, limited smart technology integration, and designs that prioritize practicality over innovation.
The Tesla Bike’s potential to integrate seamlessly with other Tesla products and its focus on user experience could set new industry standards.
Final Thoughts
The introduction of the Tesla Bike could redefine the e-bike market, pushing the boundaries of what consumers expect from electric bicycles. Its success, however, would depend on several factors:
- Market Acceptance: Convincing traditional cyclists and the broader public to adopt a high-tech, premium-priced e-bike requires demonstrating tangible benefits that outweigh the costs.
- Overcoming Challenges: Navigating regulatory landscapes, establishing robust infrastructure for charging and maintenance, and ensuring user-friendly technology are crucial steps Tesla must address.
- Competitive Response: The ripple effect on the industry could lead to accelerated innovation among competitors, ultimately benefiting consumers with more advanced and diverse options.
The Tesla Bike embodies the convergence of sustainable transportation and technological innovation. If realized, it could play a significant role in reducing urban pollution, enhancing personal mobility, and contributing to global sustainability goals.
As the landscape of personal electric transportation continues to evolve, staying informed about developments like the Tesla Bike is more important than ever.
Whether you’re a cycling enthusiast, a tech aficionado, or someone interested in sustainable living, the future of e-biking holds exciting possibilities.
We encourage you to keep an eye on industry news, explore emerging technologies, and consider how innovations in e-bikes could transform the way you navigate the world.
Embracing these advancements not only enhances your personal experience but also contributes to a more sustainable and connected global community.
FAQs
Has Tesla officially announced the Tesla Bike?
As of now, Tesla has not officially announced a Tesla Bike. This article explores the potential impact if Tesla were to enter the e-bike market.
What are the anticipated features of the Tesla Bike compared to traditional e-bikes?
The Tesla Bike is expected to feature advanced technology like AI integration, longer battery range (up to 100 miles), rapid charging capabilities, high-torque motors, and smart connectivity, surpassing the typical specifications of traditional e-bikes.
How does the Tesla Bike’s design differ from that of traditional e-bikes?
The Tesla Bike would likely have a sleek, aerodynamic design using premium materials like carbon fiber, offering a modern aesthetic. Traditional e-bikes often have more conventional designs focused on functionality.
What challenges could the Tesla Bike face in the market?
Potential challenges include regulatory compliance with varying e-bike laws, convincing traditional cyclists to adopt high-tech options, establishing charging infrastructure, and building maintenance and service networks.
How might the Tesla Bike impact the future of e-biking?
If introduced, the Tesla Bike could drive innovation in the e-bike industry, raise consumer expectations for technology and performance, and contribute to environmental sustainability by promoting electric transportation.















